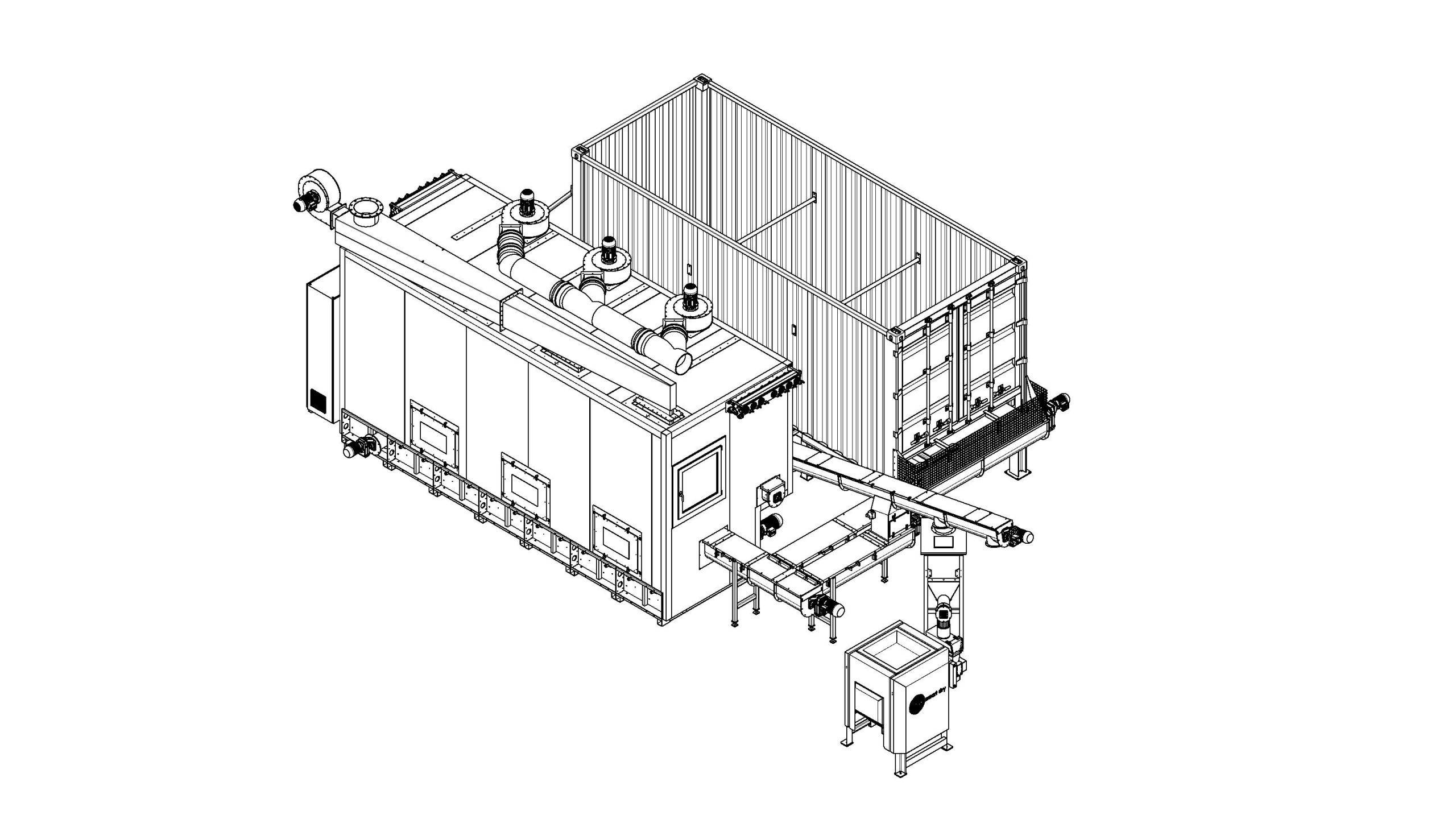
In agriculture, animal husbandry, landscape maintenance and industrial production processes for food production often result in large amounts of biomass residues. Examples of this are horse bedding, bedding from livestock farming in general.
In food production there are a large number of residues such as grape pomace in the production of wine, apple pomace in juice production, pomace in general in the extraction of fruit juices and in alcohol production, coffee grounds, bakery residues and much more. These products are usually all wet and have to be disposed of, which is usually complex and expensive.
The classic disposal route "field" is increasingly and rightly restricted, since these residues are partly hygienically contaminated. Think of sewage sludge and fattening farms, which increase the risk of harmful substances entering our food cycle through the continuous use of medicines. Uncontrolled disposal goes hand in hand with over-fertilization of the soil and entry into our groundwater.